MAP Sensor Output
![]()
While both the ST165 and ST185 models use a vane Air Flow Meter (AFM) as the primary airflow input to the ECU, all models (excluding Japanese specification ST165's) also have a Manifold Air Pressure sensor (Turbo Pressure Sensor Assy in Toyota-speak). This sensor simply measures the pressure inside the plenum chamber and sends it to the ECU as a 0-5 volt analog signal.
While the signal is used by the ECU for fuelling calculations, the most noticeable functions are operating the factory boost gauge and fuel cut.
I have used a calibrated digital manometer and a calibrated Fluke digital multimeter to perform this testing. 5V DC was applied to the MAP sensor using a PC power supply. Pressures were then applied using a Mityvac vacuum/pressure pump and the signal voltage measured using the multimeter.
Two MAP sensors were tested:
P/N 89420-17030 This sensor is fitted to the 89-Oct93 MR2 Turbo and also (using a different P/N) the ST185.
P/N 89420-17050 This sensor is fitted to the Oct93-99 MR2 Turbo and also (using a different P/N) the ST205.
Results are in the graph below.
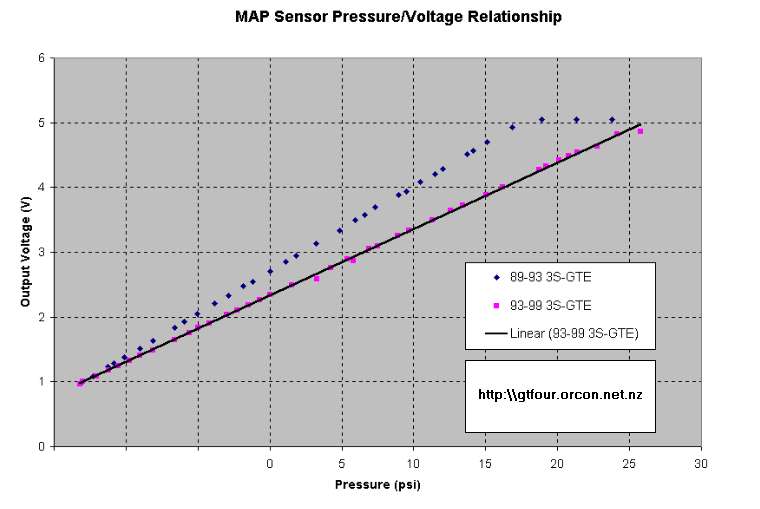
As can be seen the relationship is perfectly linear. Excuse lack of vacuum units, I couldn't be bothered working them out :-). As can be seen the ST185 sensor flatlines at about 18psi, above which it reads a constant 5.05 volts.
In contrast the ST205 MAP sensor reached 5 volts at around 26 psi. I couldn't manage higher pressures unfortunately to test higher response.
The relationships are :
ST185: V = 0.1319*psi + 2.7000 up to a maximum of 5V
ST205: V = 0.1025*psi + 2.3293 up to a maximum of 5V
Using this relationship and a simple voltage comparator circuit an adjustable boost switch relay can easily be made for operating fans, pumps etc. Better than unreliable pressure sensors.
![]()
![]()